When people think “chatbot”, it’s often not in a positive way. People conjure up images of themselves frustratingly sat by their laptop, as the conversational UI they’ve been speaking to replays the same error message over and over again. And that is certainly the case sometimes – chatbots designed by Facebook for their Messenger platform had a 70% failure rate only last year – but it doesn’t have to be.
Careful user testing, conversation mapping and error handling can help chatbots become the useful, valuable assistance tools they are designed to be. I’ve put together a list of important things to consider when designing and testing chatbots, to (hopefully) help you avoid some of the issues we’ve observed users experience when they interact with chatbots…
Avoid Jumping On The Bandwagon
One of the things you need to think about most carefully is whether a chatbot is actually the right technology for you to use: just because other companies are using them, doesn’t mean that you should. The loss of information and context caused by going from a visual interface to a text-based interface is highly likely to cause frustration if (for example) you convert a multi-step form into an unending barrage of questions!
Think of what your objectives are, and how they fit into your customers’ journey. Remember, chatbots are a tactic – not a strategy in and of themselves. If you try to make your chatbot do too much, you’re increasing the chance for error: the more you need it to do, the more testing that requires, and the more opportunity there is for human (and machine) error. If there’s another technology that could be used in place of the chatbot – test both, and see which is more effective in helping your customers accomplish their goal.
Rules of Conversation
It’s important that your bot follows traditional conversation rules – if it doesn’t, your users will find it confusing and it won’t provide them with a positive experience.
The scholar Paul Grice observed that almost all human conversations are expected to follow a basic set of rules (or maxims):
i. Maxim of Quality – people are expected to say what they understand to be the truth
ii. Maxim of Quantity – people should provide just the right amount of information to get their point across, no more, no less
iii. Maxim of Relation – people are expected to stay on the established topic
iv. Maxim of Manner – people should be direct and avoid using vague or ambiguous language
Although you should aim to adhere to all of these rules, when it comes to chatbots, the Maxim of Manner – being clear and direct – is particularly important. The clearer your responses are, the faster you’ll be able to lead users towards the dialogue path that is most relevant to their needs.
Human – But Not Too Human
Despite knowing that there’s no human on the ‘other side’ of the chatbot, most users will project characteristics on to the chatbot when using it to help them create a mental picture of the interface. You should design your chatbot’s personality to not only ‘fit’ your brand, but also to fit the service the bot is providing – this is done by looking carefully at word choice, syntax and structure.
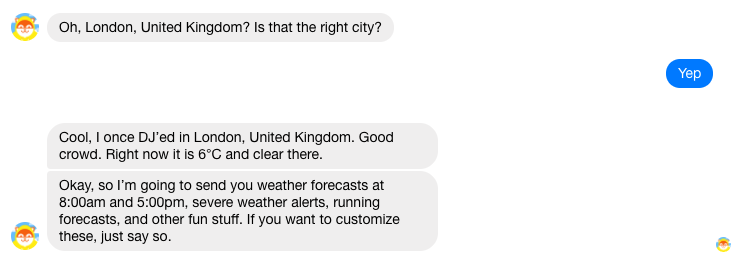
First, think about who you are designing the bot for, and draft your bot’s speech accordingly. Will your customers be looking for a companion – in which case, the tone should be informal, friendly – or an assistant (where you’d want a formal, impersonal tone)?
The type of content your bot provides will also dictate the tone of its speech. If your bot is news-focused or meant to guide users through a process involving payments or other sensitive information, a formal and authoritative tone is advisable.
In cases where the chatbot can be more light-hearted in tone, it’s still important to test which phrases resonate with users, and which are perhaps a step too far. For example, some users may prefer the chatbot they’re using to say “OK”, instead of the much more casual “Cool”.
To Be Visual, Or Not To Be Visual
Unlike Voice Controlled User Interfaces (VCUIs) like the Amazon Echo, chatbots allow you to add visuals and emojis to the dialogue… whether you should or not is a different matter!
If you decide to use visuals in your chatbot, you must be sensitive to all the different ways users can interpret these. You may think an image of a filled Champagne glass connotes a celebration – but some of your users may jump to the conclusion that you’re promoting alcohol consumption. It’s also very important to be aware of images that have religious or cultural associations, as these can cause offence.
Visual cues such as a “typing” symbol or message can be used if you want to show that the bot is responding, and not overload the user by giving them too much information at once. This is particularly useful if your interface generally takes a second or two to load its responses, as it will also reassure the user that the system is working!
Test, Analyse, Fix – Then Test Again!
Unfortunately (but unsurprisingly), users will not always use interfaces like chatbots in the way we design for, even with the most meticulously designed flows. However, there are some key things to look out for when testing:
- Length of responses– Test out different ways of presenting information – such as breaking up the response into multiple boxes, or presenting them in bullet point format – if there’s a lot you need to convey
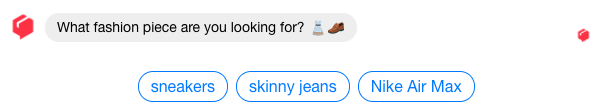
- Response buttons– including buttons in the chat that give your users prompts regarding how to respond. Testing will help you to understand at which stages of interaction the buttons are most useful, and where it may be better to allow free text
- Language variants– shorthand and acronyms are very common in human-to-human messaging, so it makes sense that some people will opt to type this way when communicating with chatbots. Test out which are the most common and make sure your system is able to process them.
- Acknowledgements– test out whether your respondents want the bot to acknowledge the answer or comment it has just recieved (this could be viewed as reassuring or annoying – you won’t know until you test!), or if it should directly continue the conversation
- Re-prompting– in cases where the bot doesn’t understand what the user has said, test whether a re-prompt (“I didn’t quite catch that – could you explain it to me again?”) or explicit help dialogue is preferred
At Bunnyfoot, we’re experts at understanding consumer needs and running user testing to optimise products and services, based on evidence. If you’re keen to learn more about designing and building chatbots, we’d love to hear from you!
Find out more:
- Blog: The Importance of UX When Designing Chatbots / Voice User Interfaces
- Blog: The Difference Between Chatbots and Voice User Interfaces
- Training Course: Certified Practitioner in UX




